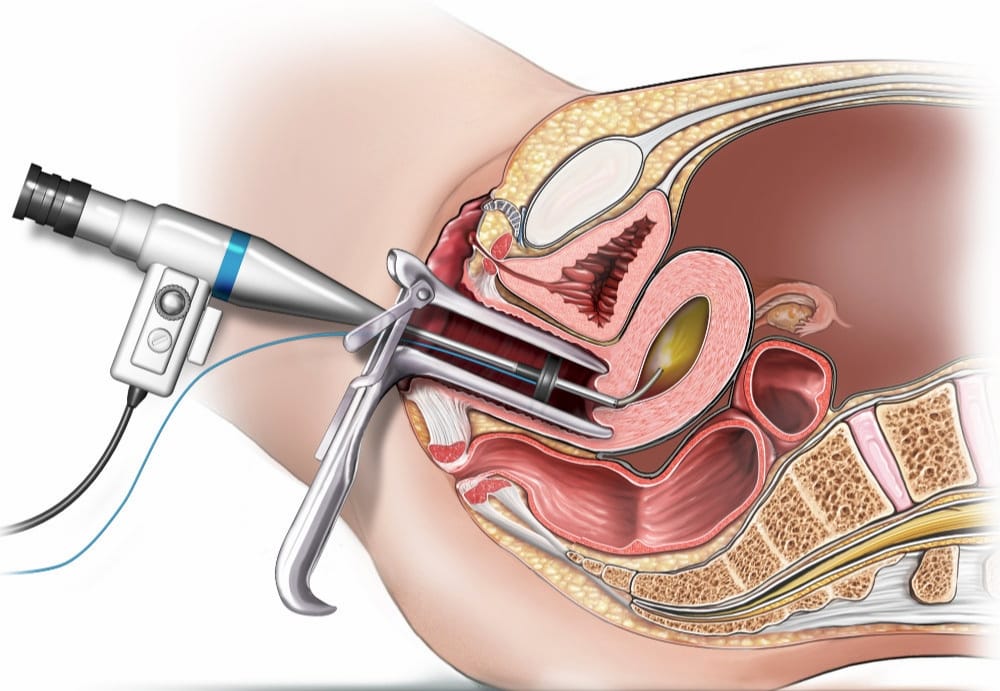
Hysteroscopy: A Key to Women's Health
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat conditions affecting the uterus. It involves the use of a hysteroscope, a thin, lighted tube inserted through the vagina, to view the inside of the uterus. This procedure is commonly used for both diagnostic and operative purposes, offering women effective solutions for various gynecological issues.


Types of Hysteroscopy
1. Diagnostic Hysteroscopy
-
Used to identify abnormalities inside the uterus.
-
Commonly performed to investigate symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, infertility, or recurrent miscarriages.
2. Operative Hysteroscopy
-
Used to treat issues detected during diagnostic hysteroscopy.
-
Allows for the removal of fibroids, polyps, adhesions, or other uterine abnormalities.
When is Hysteroscopy Recommended?
-
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Helps identify the cause of heavy, irregular, or postmenopausal bleeding.
-
Fibroids or Polyps: Detects and removes non-cancerous growths within the uterus.
-
Uterine Septum: Diagnoses and corrects congenital abnormalities in the uterine structure.
-
Infertility or Recurrent Miscarriages: Evaluates uterine health to improve the chances of a successful pregnancy.
-
Retained Products of Conception: Removes remaining tissue after a miscarriage or childbirth.
-
IUD Issues: Locates and safely removes displaced or embedded intrauterine devices.
Benefits of Hysteroscopy
-
Minimally Invasive: No external cuts; the procedure is performed through the vagina.
-
Quick Recovery: Most patients return to normal activities within 1–2 days.
-
High Precision: Provides a clear, direct view of the uterine cavity for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
-
Combination Capability: Can be performed along with laparoscopy for more comprehensive treatment when needed.
Recovery After Hysteroscopy
-
Timeframe: Most women recover within 1–2 days, with possible mild cramping or light spotting.
-
Follow-Up: Postoperative appointments help monitor healing and manage any concerns.
-
Postoperative Care: Avoid heavy lifting and sexual intercourse for a short period, as advised by your doctor.